Experience Mapping: Create Better User Journeys

Experience mapping demonstrates user interaction with software products to achieve goals. It aims to understand how users feel and the frustrations they encounter with the product itself. This tells us how people see a given software product, and this article will explain how to design the best user journey.

Discover how at OpenReplay.com.
It is important to map the software development process as it helps teams understand what users want or require. Teams use this information to enhance their solutions by pinpointing troubles and advantages aimed at satisfying their customers’ requirements, which results in customer satisfaction.
In this article, we will discuss key aspects of creating an experience map, such as user personas, which are prototypes for average users and their characteristics, and a user journey, which signifies all the steps people take from their first introduction to an organization until they attain whatever they want.
What is Experience Mapping in Software Development?
Organizations strategically use Experience Mapping in software development processes to show how users relate to products. It goes beyond user flows, including users’ feelings when they interact with a client’s application or website. The latter are issues that customers encounter and that provide opportunities for improving user-friendliness and user experience.
Benefits of Experience Mapping
During software development, teams benefit a lot from experience mapping. This is when the teams get to be customers, determine what the users require, and get an in-depth perspective of a user journey, which refers to the needs, behaviors, and emotions of consumers considered collectively. This assists organizations in becoming familiar with their users more profoundly, and henceforward more remarkable determinations approach enhancement of their products.
Experience maps are used to show areas where users can find challenges. These areas can make a user frustrated; they are called pain points. Ensure that such problems are identified quickly, enabling organizations to improve in such sectors. Mapping helps teams get creative by making it easier for companies to not only develop products that will make them remain very competitive in the market but also meet the requirements and overall user experience of their customers when they return to a product.
Steps in Creating an Experience Map
When creating experience maps, there are certain steps one must follow for accurate information and results.
Research and Data Collection
Conducting interviews, or doing a user observation could offer you an understanding of the experiences they undergo, what they lack, and the problems they encounter.
These informal but effective studies carried out within a company benefit the users, enabling them to express themselves freely without fear.
Identifying User Personas
User Personas are fabricated human figures intended to mirror individual user groups that may use a service, product, site, or brand the same way. This makes it easier for the design teams to understand users, help with the design-making process, ensure good communication design, ensure user needs, focus on the user goals, and emphasize the features that need to come first.
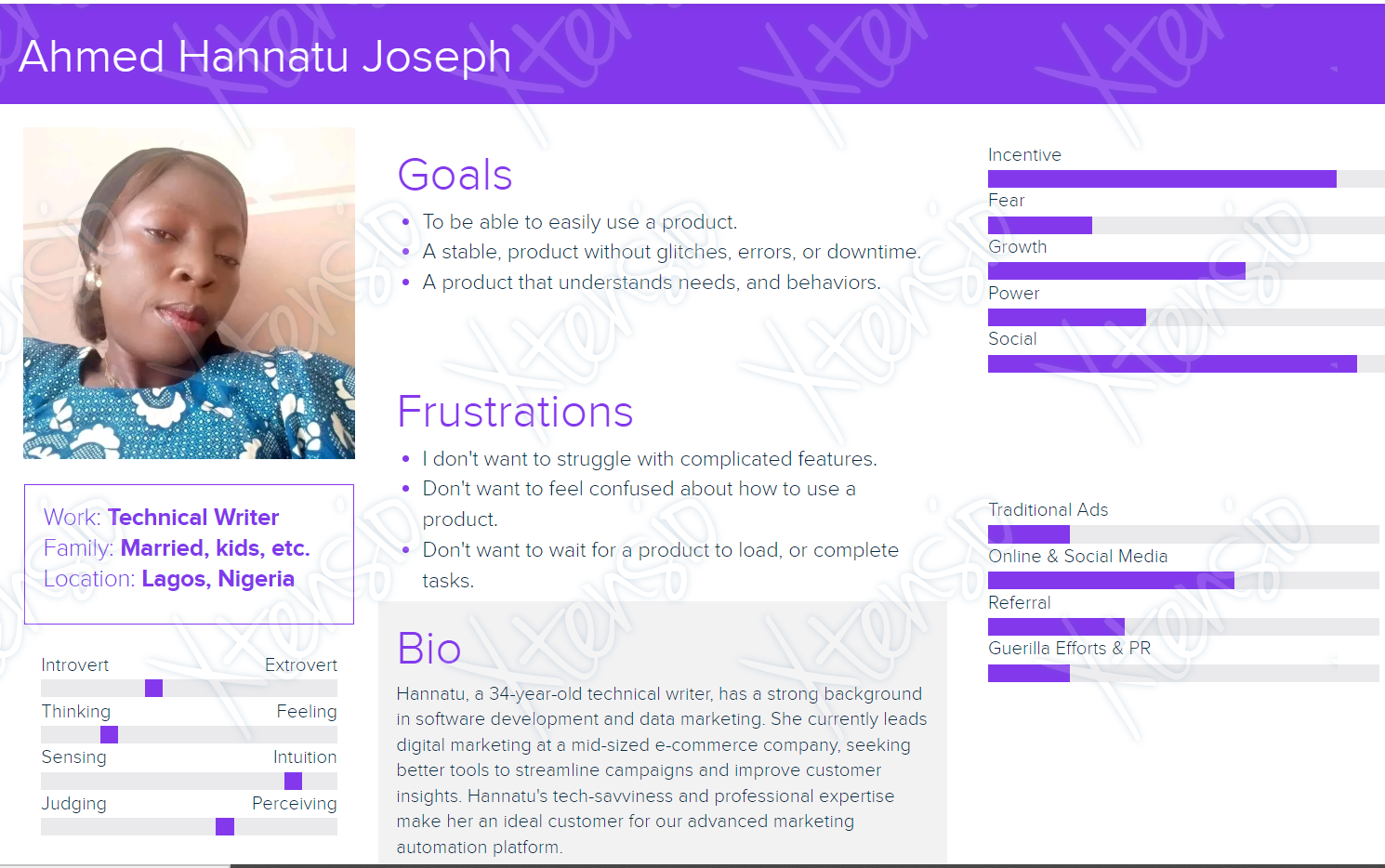
To create detailed personas, there are specific actions that have to be taken, and some of them include:
- Doing User Research: User data, both narrative and numerical, is collected from the participants through surveys, interviews, and analytical tools.
- find User Patterns: This involves classifying users based on their behavior or demographics.
- Develop a Persona Profile: Using false names and stories alongside other detailed information on a step-by-step basis is required for creating persona profiles. Establish what someone wants when they use the service or product through these personas (objectives and frustrations).
- Visual Design: Make them visually appealing so the user can interact with them through images or humans representing these characters in your software. Making it easy to use.
- Validation and Refinement: Obtain feedback from the team and refine their personas.
- Application and Upkeep: Employ personas during the design process and ensure they are up-to-date.
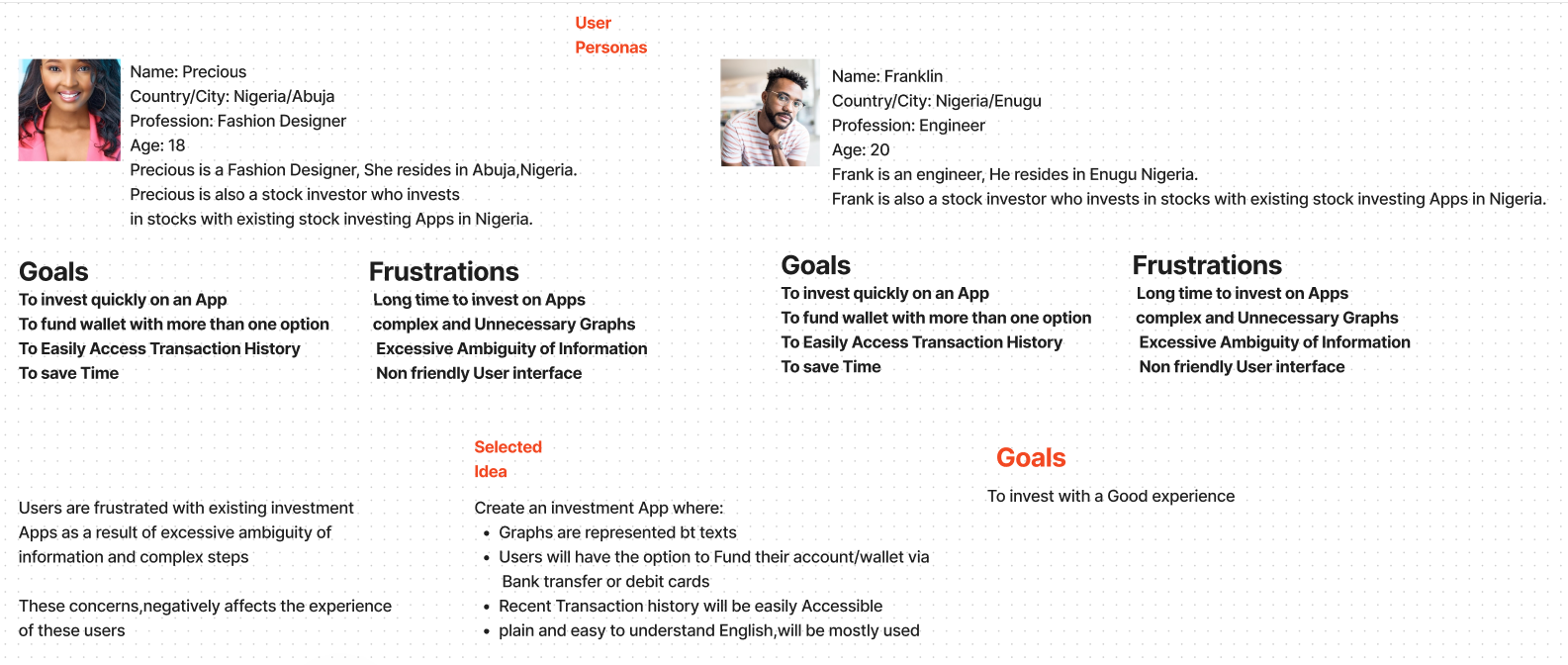
Mapping the User Journey
The user journey maps out how people move when using a product or service. This step makes it possible to visualize how end users experience it, find out its weak points, where it could be improved, and when they are happy. Appreciating the course helps make users’ experiences continuous and involving by meeting their requirements at all stages.
Categorize the user journey into distinct phases, e.g. awareness, consideration, purchase, and post-purchase. Every stage stands for one step in the way a user interacts with your product or service. Recognize different areas of contact between consumers and your brand, such as website, customer support services, physical stores, and other social networks. By identifying these areas, one gets to locate better where users engage most with your product or service.
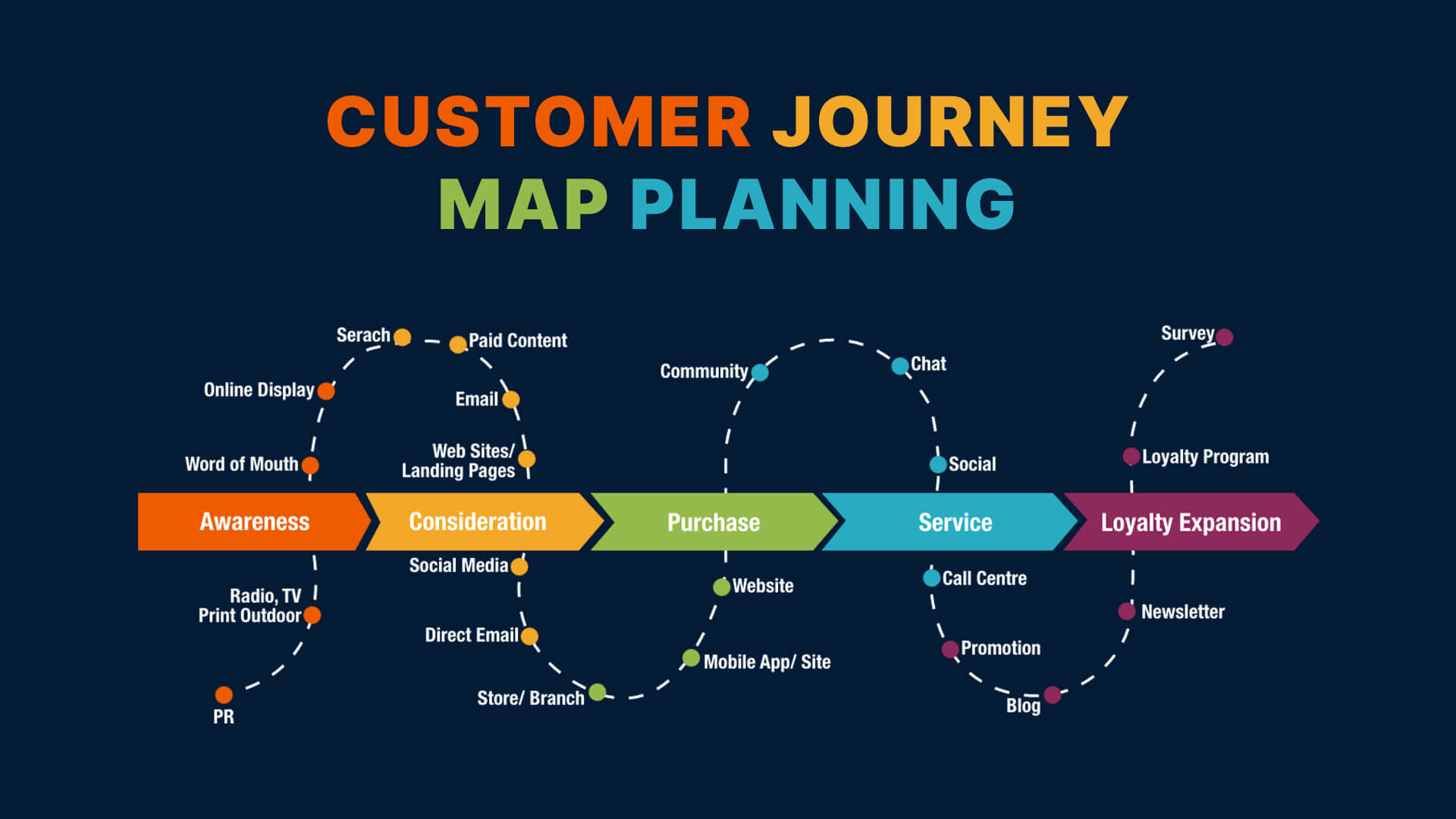 (source:https://www.codecademy.com/resources/docs/uiux/journey-map)
(source:https://www.codecademy.com/resources/docs/uiux/journey-map)
Create a map of users’ feelings at each stage and touchpoint. Understanding how users feel in terms of excitement, frustration, or happiness will enable you to satisfy their demands effectively, hence promoting positive experiences across the journey.
Analyzing and Synthesizing Data
Once the user data has been gathered, it should be analyzed and combined meaningfully to better understand it. So, during user research results interpretation, study how users behave when interacting with various products, and look out for behaviors that usually repeat themselves and indicate frustration or need issues. This step helps organize the information and gather related data to identify patterns among them.
When you do this, discover the main ideas that show big user needs, engineering factors, and difficulty points. By pointing out the main ideas, it is possible to prioritize some areas to improve user experience and make the product closer to what users want.
Visualizing the Experience Map
Involvement in designing a detailed and visually appealing experience map that represents the user’s journey when using your product or service paves the way for understanding the kind of experience that different stakeholders can identify pain areas and propose areas of improvement. Through adherence to the principles of good design and the application of appropriate tools, one can create a highly informative experience map that serves as a guide in making better decisions.
To achieve a better understanding of an experience map, you need to comply with major design principles, which include:
- Clarity: It is important that while being read, it should be seen or called so that its content can be understood easily without excesses and with proper arrangement. Simplicity: Concentrating on the significant fragments of the user pathway eliminates any disorder within the chart. Consistency: Ensure that the drawing maintains coherence through identical colors, letter types, and symbols.
- Show the user’s feelings and experiences in every phase to build a connection and understanding with those involved (stakeholders).
- Accountability: Develop the map in such a way that it shows places to improve and provides actionable insights that are useful in making design choices.
There are different tools that an individual can use to generate specific and attractive experience maps. For instance, the use of software such as Adobe XD, Sketch, and Figma facilitates an accurate map. Among them are Smaply, UXPressia, and Miro, which are specialized programs that include templates and features meant for road mapping. Moreover, you can adapt general visualization tools like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, or Canva for making experience maps.
Implementing Experience Maps in Software Development
Mapping user experiences into the software development process ensures that user perceptions lead directly to product design and operation, bringing them closer.
Agile and Iterative Development
For software development to remain targeted at addressing user needs and challenges, use experience maps for the development and ranking user stories within the product backlogs. Using experience map insights guides the choice of features and tasks to advance the user experiences during sprint planning.
For continuous product improvement, use feedback from users to draw lessons from the results of the tests conducted in each iteration by updating the experience maps regularly.
Cross-Functional Team Collaboration
Sharing experience maps with every team member is a way to boost mutual comprehension of users’ trajectory and objectives, which also involves developers, designers, and stakeholders.
Another factor is the facilitation of workshops, which include a variety of disciplines aimed at interpreting and discussing customer journey maps by offering collaborative insights leading to possible remedies. Experience map findings should fit into all staff operations so that they can think of users at the center of their work.
When experience maps are integrated into agile and iterative development and you promote cross-functional teamwork, a more user-centered approach to product development can be realized.
Using Experience Maps to Inform Design Decisions
Experience maps give valuable information that will help in making decisions when designing something and ensuring it meets its users’ expectations. Use experiences gained through mapping out to implement user-centered design principles, where you concentrate on making easy and interesting user interfaces, amongst others. This includes giving more attention to what the users want as well as their preferences while designing a product rather than using one’s judgment alone.
Experience maps can be used to identify pain points and areas where usability and accessibility need improvement. When you understand how users interact and their problems, you can create interfaces that are friendlier to everyone and more accessible, thus ensuring no user experiences a problem.
Prioritizing Features and Improvements
Using experience maps aids in ranking functions and improvements by showing those areas in a person’s way that are important, either positively or negatively. Therefore, employ them to highlight top user needs and pain points. This way, consider how such products can be upgraded for greater user satisfaction.
When choosing features, consider technical restrictions while using expert design examples to achieve an optimal user experience. Work around the constraints of your technical feasibility so those most affected by the changes can adapt easily.
Best Practices
To craft experience maps effectively, comprehend the typical hurdles and devise tactics to surmount them, besides adhering to ways of constructing powerful maps. Common Problems and their Solutions:
- Incomplete or Inaccurate Data: One way to prevent incomplete or inaccurate data is by conducting extensive and varied research to collect exhaustive and dependable knowledge.
- Absence of Stakeholder Buy-In: To ensure that the stakeholders fully buy into the value of experience maps, always communicate with them and engage them in map development.
- Up-to-date Maps: Always refer back to and update our experience maps to keep them in line with the most recent software developments and tools people use by getting new information and additional user feedback.
- Data Bias: Awareness about potential bias in datasets within your possession is required, and one must actively look for various outlooks.
- Overly Complex Maps: The main thing to remember about overly complex maps is that they should be clear and focused on the most critical parts of the user journey.
Tips for Effective Experience Mapping
Begin with clear goals for your experience mapping that will guide the entire process. Involve different groups within your organization. Encourage employees working in different departments to bring out various views. Employ graphical tools, add icons, color coding, and flowcharts so that the map is more interesting and attractive while enhancing comprehension.
Make sure you periodically review the experience map and make adjustments using the new information and feedback from the user to help maintain its accuracy. Include users’ emotional experiences in it to help you understand their journey, leading to possible areas of improvisation.
Tools and Techniques for Experience Mapping
Modern software solutions and traditional methods are used to create experience maps effectively. Although the traditional approach is becoming less popular nowadays, many organizations still use it because they believe that hands-on training provides better results than other methods, such as using computers or mobile devices.
Miro is an online collaborative whiteboard platform that allows teams to easily create detailed experience maps and choose from different templates and visualization tools. Lucidchart supports experience mapping with its simple interface and enormous library of figures and templates, making it possible for users to design explicit and expert maps.
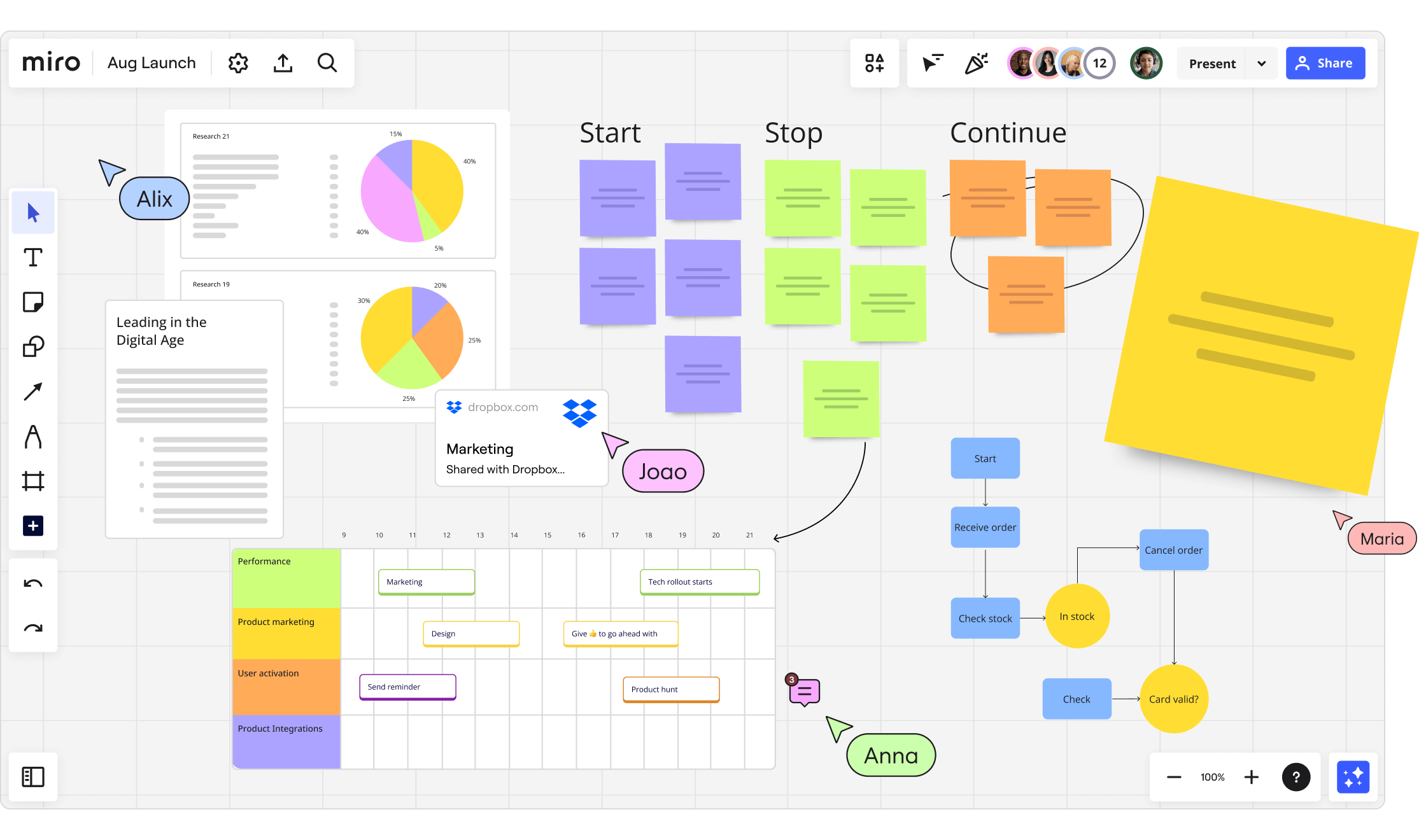 (source:https://miro.com/about)
(source:https://miro.com/about)
Traditional Methods like sticky notes, which is a practical approach where group members can put down steps in the user journey, pain points, and insights on sticky notes and then group them on a wall or board. This kind of approach involves great interaction thus promoting teamwork.
 (source: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/what-sticky-notes-its-benefits-uses-atul-garg)
(source: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/what-sticky-notes-its-benefits-uses-atul-garg)
The usage of whiteboards helps in sketching out what is entailed in user journeys and mapping experiences, which enables instantaneous adjustments and brainstorming. It is mostly preferred when conducting repeated meetings and promoting group discussions.
Conclusion
Experience mapping involves more than just using a tool; instead, it involves a transformative process that allows people to put themselves in the shoes of their users and see the world as they see it. Genuine understanding and empathy for the pathways or journeys these people take should enable the design conceptualization team or product development team to generate offerings that add value to meet their wants.
For better comprehension and optimization of user journeys, teams can utilize the powerful mapping experience technique, which allows them to illustrate interactions, locate troubled areas, and identify how to improve them. Businesses thus optimize user-oriented products and services by adopting experience-mapping best practices, employing appropriate tools, and enhancing cross-departmental collaboration.
Ensuring that experience maps stay useful and can be improved by being continuously updated with user feedback and new information would result in improved business outcomes in terms of usability as long as they are still relevant.
References
If you’re still interested in more readings or information about maps that show customer experiences, here are some books, articles, or online resources you might want to check out:
- Mapping Experiences by Jim Kalbach
- This is Service Design Thinking by Marc Stickdorn and Jakob Schneider
- The User Experience Team of One by Leah Buley
- Mapping the Customer Journey by Forrester
- All You Need to Know about Customer Journey Mapping by Smashing Magazine
- Nielsen Norman Group’s UX Research and Reports
- UX Design Institute’s Blog and Case Studies
- Interaction Design Foundation’s Encyclopedia and Courses
Gain control over your UX
See how users are using your site as if you were sitting next to them, learn and iterate faster with OpenReplay. — the open-source session replay tool for developers. Self-host it in minutes, and have complete control over your customer data. Check our GitHub repo and join the thousands of developers in our community.

