Is It Time for the JavaScript Temporal API?
Date handling in JavaScript is ugly. The Date() object has not changed since the first Java-inspired implementation in 1995. Java scrapped it but Date() remained in JavaScript for backward browser compatibility.
Issues with the Date() API include:
- it’s inelegant
- it only supports UTC and the user’s PC time
- it doesn’t support calendars other than Gregorian
- string to date parsing is error-prone
Dateobjects are mutable — for example:
const today = new Date();
const tomorrow = new Date( today.setDate( today.getDate() + 1 ) );
console.log( tomorrow ); // is tomorrow's date
console.log( today ); // is also tomorrow's date!Developers often turn to date libraries such as moment.js but it’s a 74Kb payload and dates remain mutable. Modern alternatives such as Day.js and date-fns may be better but should a library necessary when your app has minimal date-handling requirements?
Browsers must continue to support Date() but a new Temporal static global date object is at the Stage 3 Candidate Proposal in the TC39 standards approval process (the final stage before implementation). The API addresses all the issues above and it’s coming to the Chrome browser soon. It’s unlikely to have widespread implementation until late 2022 so be wary that changes could occur.
Current Date and Time
Temporal.Now returns an object representing the current date and time. Further methods provide information such as:
// time since the Unix epoch on 1 Janary, 1970 UTC
Temporal.Now.instant().epochSeconds;
Temporal.Now.instant().epochMilliseconds;
// time in current location
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO();
// current time zone
Temporal.Now.timeZone();
// current time in another time zone
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO('Europe/London');Instant Dates and Times
Temporal.Instant returns an object representing a date and time to the nearest nanosecond according to an ISO 8601 formatted string:
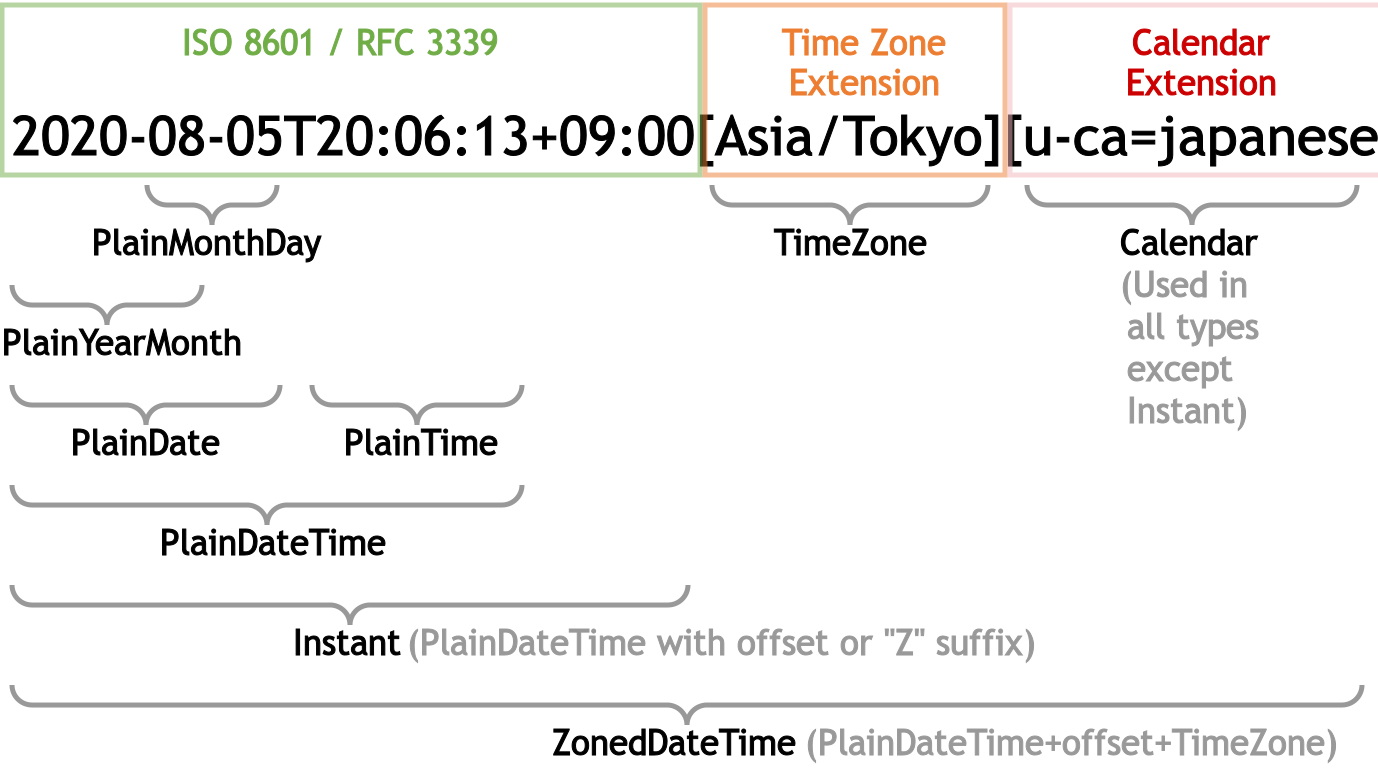
Temporal.Instant.from('2022-03-04T05:56:78.999999999+02:00[Europe/Berlin]');
Temporal.Instant.from('2022-03-04T05:06+07:00');You can also use an epoch value:
Temporal.Instant.fromEpochSeconds(1.0e8);Zoned Dates and Times
Temporal.ZonedDateTime returns an object representing a timezone and calendar-aware date/time at the instant an event occurred (or will occur) in a particular global location, e.g.
new Temporal.ZonedDateTime(
1234567890000, // epoch nanoseconds
Temporal.TimeZone.from('Europe/London'), // timezone
Temporal.Calendar.from('iso8601') // default calendar
);
Temporal.ZonedDateTime.from('2025-09-05T02:55:00+02:00[Africa/Cairo]');
Temporal.Instant('2022-08-05T20:06:13+05:45').toZonedDateTime('+05:45');
Temporal.ZonedDateTime.from({
timeZone: 'America/New_York'
year: 2025,
month: 2,
day: 28,
hour: 10,
minute: 15,
second: 0,
millisecond: 0,
microsecond: 0,
nanosecond: 0
});Plain Dates and Times
Plain dates and times reference simpler calendar events which are not associated with a specific time zone. The options include:
-
Temporal.PlainTimerefers to a specific time, e.g. “the meeting occurs at 3pm every weekday”:// both are 15:00:00 new Temporal.PlainTime(15, 0, 0); Temporal.PlainTime.from('15:00:00'); -
Temporal.PlainDaterefers to a specific date, e.g. “your tax return is due by January 31, 2022”:// both are January 31, 2022 new Temporal.PlainDate(2022, 1, 31); Temporal.PlainDate.from('2022-01-31'); -
Temporal.PlainDateTimerefers to a date and time without a time zone:// both are 4 May 2022 at 10:11am and 12 seconds new Temporal.PlainDateTime(2022, 5, 4, 10, 11, 12); Temporal.PlainDateTime.from('2022-05-04T10:11:12'); -
Temporal.PlainYearMonthrefers to a date without a day, e.g. “the June 2022 schedule is ready”:// both are June 2022 new Temporal.PlainYearMonth(2022, 6); Temporal.PlainYearMonth.from('2022-06'); -
Temporal.PlainMonthDayrefers to a date without a year, e.g. “Star Wars day is on May 4”:// both are May 4 new Temporal.PlainMonthDay(5, 4); Temporal.PlainMonthDay.from('05-04');
Open Source Session Replay
OpenReplay is an open-source, session replay suite that lets you see what users do on your web app, helping you troubleshoot issues faster. OpenReplay is self-hosted for full control over your data.
Start enjoying your debugging experience - start using OpenReplay for free.
Date and Time Values
You can extract specific date and time values from a Temporal object. Assuming the following date and time:
const t1 = Temporal.ZonedDateTime.from('2022-12-07T03:24:30+02:00[Africa/Cairo]');you can extract:
t1.year; // returns 2022
t1.month; // 12
t1.day; // 7
t1.hour; // 3
t1.minute; // 24
t1.second; // 30
t1.millisecond; // 0
t1.microsecond; // 0
t1.nanosecond; // 0Other useful properties include:
dayOfWeek— returns1for Monday to7for SundaydayOfYear— returns1to365or366on leap yearsweekOfYear— returns1to52or53daysInMonth— returns28,29,30, or31daysInYear— returns365or366inLeapYear— returnstruefor a leap year orfalsewhen not
Comparing and Sorting Dates and Times
All Temporal objects have a .compare(date1, date2) method which returns:
0whendate1anddate2are the same1whendate1occurs afterdate2, or-1whendate1occurs beforedate2
For example:
const
date1 = Temporal.Now,
date2 = Temporal.PlainDateTime.from('2022-05-04');
Temporal.ZonedDateTime.compare(date1, date2);
// returns 1 when May 4, 2022 arrivesYou can pass the compare() method as an Array sort() function to arrange dates into ascending chronological order (earliest to latest):
const t = [
'2022-01-01T00:00:00+00:00[Europe/London]',
'2022-01-01T00:00:00+00:00[Africa/Cairo]',
'2022-01-01T00:00:00+00:00[America/New_York]'
].map( d => Temporal.ZonedDateTime.from(d) )
.sort( Temporal.ZonedDateTime.compare );Date and Time Calculations
All Temporal objects offer math methods to add(), subtract(), or round() to a duration.
You can define a duration as a Temporal.Duration object which sets a period in years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes, seconds, milliseconds, microseconds, and nanoseconds as well as a sign for -1 negative or 1 positive durations. However, all these methods accept a duration-like value without the need to create a specific object. Examples:
const t1 = Temporal.ZonedDateTime.from('2022-05-04T00:00:00+00:00[Europe/London]');
// add 8 hours 59 minutes
t1.add({ hours: 8, minutes: 59 }); // or
t1.add(Temporal.Duration.from({ hours: 8, minutes: 59 }));
// subtract 2 weeks
t1.subtract({ weeks: 2 }); // or
t1.add({ weeks: 2, sign: -1 });
// round to nearest month
t1.round({ smallestUnit: 'month' });Plain dates and times can wrap so adding 24 hours to a PlainTime returns a new Temporal object with an identical value.
The until() and since() methods return a Temporal.Duration object describing the time until or since a specific date and time based on the current date/time, e.g.
// months to t1
t1.until().months;
// days to t2
t2.until().days;
// weeks since t3
t3.since().weeks;The equals() method also determines whether two date/time values are identical:
const
d1 = Temporal.PlainDate.from('2022-01-31');
d2 = Temporal.PlainDate.from('2023-01-31');
d1.equals(d2); // falseFormatting Date and Time Strings
All Temporal objects have a string representation returned when using the .toString() method, e.g. Temporal.Now.toString():
2022-09-05T02:55:00+02:00[Europe/London]This is not user friendly but the Internationalization API offers a better alternative with localisation options. For example:
// define a date
const d = new Temporal.PlainDate(2022, 3, 14);
// US date format: 3/14/2022
new Intl.DateTimeFormat('en-US').format(d);
// UK date format: 14/03/2022
new Intl.DateTimeFormat('en-GB').format(d);
// Spanish long date format: miércoles, 14 de abril de 2022
new Intl.DateTimeFormat('es-ES', { dateStyle: 'full' }).format(d);This is not part of the Temporal API and there’s no guarantee the Intl (Internationalization) API will support Temporal as well as Date objects — although there would be a developer outcry if it didn’t!
Temporal Time
We’ve accepted the dodgy Date() since day one but Temporal gives JavaScript developers something to look forward to. The days of resorting to a date library are nearly over.
For further information, refer to: